How Voltraware is Powering Micromobility Solutions Using AirFuel Resonant
Established in 2019, Voltraware is a fabless semiconductor company specializing in the research and development of integrated circuits for wireless power transfer applications. Their technology is based on magnetic resonance, meaning it can charge multiple devices at a distance without the need for a precise alignment between the transmitter and receiver.
Products that use Voltraware’s semiconductor chips for wireless charging are automatic, reliable, and safe. The wireless power receiver automatically starts charging the battery when it enters the transmitter’s charging zone. Thanks to 에어퓨엘 공진방식 기술™ wireless charging technology, eBikes and eScooters that use Voltraware’s chips for wireless charging can simply “park and charge,” eliminating the need for both repeated plugging or unplugging of cables as well as exposed metal contacts and power ports.
The result? Wirelessly charged micromobility solutions made for reliable, public use in today’s smart cities.
The Challenge: Create a Better Charging Solution for eBikes & eScooters
For micromobility operators, the solutions available for charging their eBikes and eScooters was a major pain point. Between wired charging and swapping batteries, both had their drawbacks.
Traditional wired charging has high operational overhead due to labor costs and wear-and-tear on the cables and charging ports. Meanwhile, battery swap—where a used battery is manually removed and replaced with a fully charged battery, is a costly capital expense for the operators on the spare batteries required for their deployed vehicles.
Voltraware saw an opportunity to improve on the approach to charging electric micromobility devices in today’s smart cities.
Specifically, they sought to offer wireless power ICs and hands-free low maintenance wireless charging solutions to innovative companies for the design and integration of wireless power enabled eBikes and eScooters.
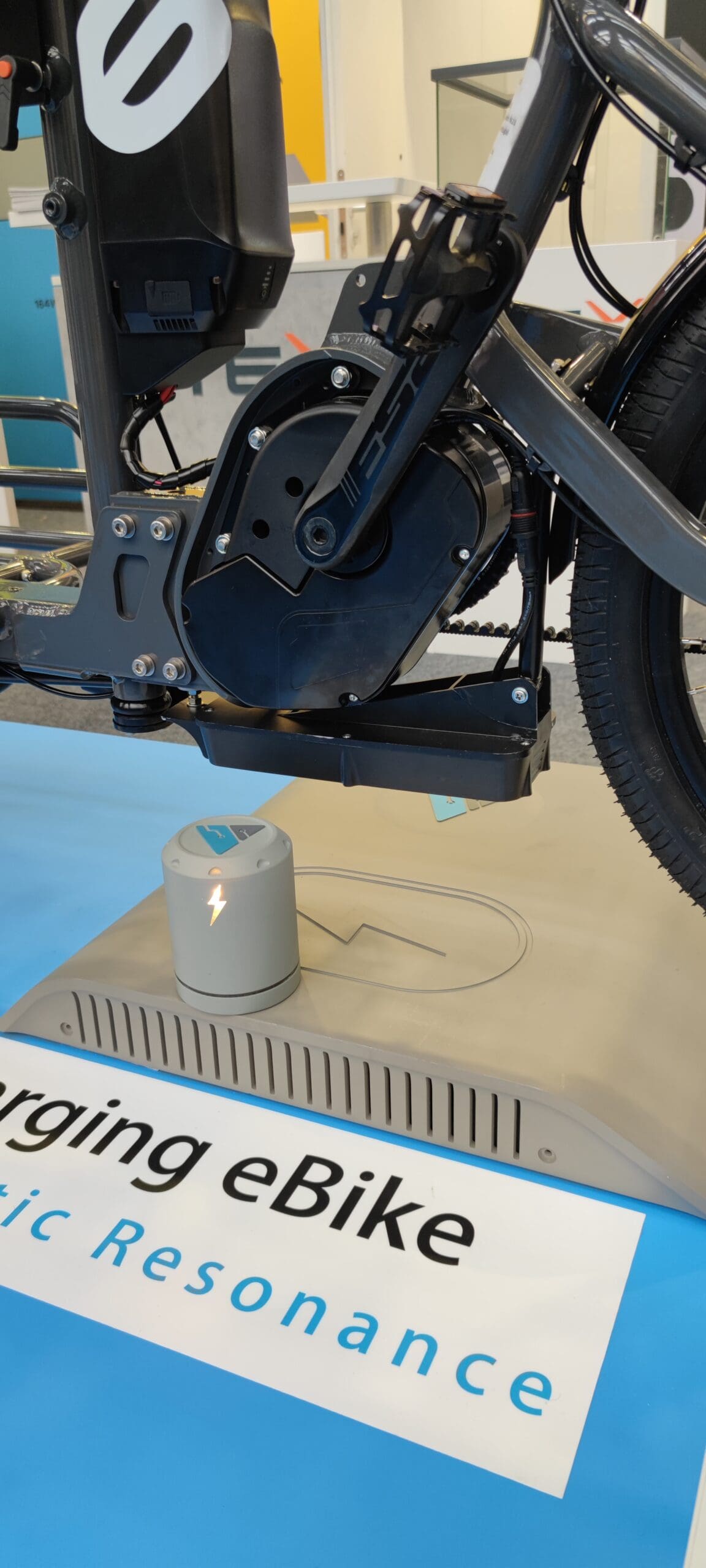
This goal would allow micromobility operators to utilize wireless charging hands-free and at a distance without the need for precise alignment between the transmitter and receiver. Rather than wires or battery swaps, the approach utilizes a Power Transmitting Unit that operates in magnetic resonance with a Power Receiving Unit to achieve wireless charging in a “beneath charging” configuration. In addition to addressing a primary pain point of micromobility operators, the technology also provides an improved user-experience for customers.
The Solution: A Two-Part System Utilizing AirFuel Resonant Technology
Voltaware brought together its IC, application, and marketing teams to identify an approach that would raise the bar on technology within the micromobility sector. To start, they chose Voltraware’s VW8000 wireless power controller IC together with an innovative coil design and system design.
Then, integrating AirFuel Resonant technology, they built a two-part system that works in tandem to provide wireless charging to the solution. A T32 Power Transmitting Unit sits inside a charging pad enclosure on the ground, while a R32X series Power Receiving Unit resides inside a vehicle side enclosure under an eBike’s motor. Working as a pair, the system not only achieves eBike and eScooter wireless charging, but also does so at a longer coil-to-coil distance than required by the “beneath charging” configuration.

With this solution, Voltraware was able to directly address the needs of the micromobility market. Gary Chi, Director of Technical Marketing at Voltraware explains,
“The idea of wireless charging for Shared MicroMobility vehicles is to introduce Opportunistic and Hands-Free battery charging into the shared ecosystems of the operators. The goal of wireless charging is to increase the utilization rate of the shared vehicles while extending the lifecycle of their batteries – two of the biggest levers the shared operators can pull for profitability!” – Gary Chi, Voltraware
The solution is compatible with 36V, 48V, or 52V eBike battery systems with just four easy steps:
- Determine the Z Level of your Power Receiving Unit. Z Level is the measured distance from the charging surface of the PTU to the underside of the PRU (typically referred to as the “coil-to-coil” distance).
- Determine the Power Class of your Power Receiving Unit. There are 3 Power Classes for the Power Receiving Unit: PC1 = 80W, PC2 = 150W and PC3 = 250W.
- Determine the Charging Voltage of your Power Receiving Unit. What is the DC output voltage of the battery pack used for your eBike or eScooter?
- Select an Interoperable Power Transmitting Unit for your Power Receiving Unit. From STEP 1 – 3, the Z Level, Power Class, and Charging Voltage have been determined for the Power Receiving Unit. The Power Transmitting Unit’s Z Level and Power Class shall be equal or greater than the Power Receiving Unit.
The Results: User-Friendly, Wireless Public Charging Stations
This solution succeeded, giving both operators and users reason to celebrate. Challenged with a mere 0.035 coupling coefficient “beneath charging” use-case, the T32 + R32X approach still achieved above 72% DC-to-DC system efficiency at a coil-to-coil distance of Z= 14-17cm and the X, Y misalignment tolerance of +- 3cm. If adopted, this combination can immediately help reduce the operational overhead for the charging of shared micromobility vehicles deployed and owned by operators.
Voltraware’s micromobility wireless charging solution also addressed the pain points of battery swap charging to provide benefits like:
Increased Utilization Rate
- Higher average State-of-Charge (SoC) of the vehicles can be maintained with the shared ecosystem.
- In-service vehicles are sustained on a 24-7 basis without the need for manual battery swap.
Extended Battery Life
- The on-vehicle battery is typically “shallow” charged at (70% – 90%) SoC.
- Frequent and smaller charging periods avoid overheating the batteries.
Reduced Operating Cost
- With a higher average SoC, the average size of the on-vehicle batteries can be reduced.
- Swap/spare batteries are no longer necessary.
- No labor and no wear and tear involved in battery charging.
This combination can immediately help reduce the operational overhead for the charging of shared micromobility vehicles deployed and owned by operators.
In addition to addressing a major point of the micromobility sector, public eBike and eScooter users benefit from a unique “Park and Charge” user experience that’s seamless and easy to navigate, making this fun, popular and eco-friendly mode of transportation more accessible than ever in cities across the world.
As an active member of AirFuel Alliance, Voltraware is leading the development of a global technology standard for micromobility wireless charging. Look out for announcements of this new AirFuel standard, as it’s sure to make waves in the market and further accelerate the adoption of wireless charging!
The micromobility market has exploded in recent years, and the next step for these devices is to adopt next-gen wireless charging. Beyond eBikes and eScooters, products like drones, lawn mowers, and snow blowers are poised to benefit from the upgrade to AirFuel Resonant wireless charging, which will enable them to charge multiple devices at once without requiring precise placement and on a single transmitter point.
Working Together to Create a Wire-Free World
As a member of AirFuel Alliance, Voltraware used AirFuel’s next-gen wireless power technology to bring a better solution to market, and their work on AirFuel’s micromobility standard is primed to shape the market.
에어퓨엘 연합 enables companies to provide cutting edge wireless charging and wireless power experiences for their customers. Members bring wireless power solutions to market today and champion innovation to advance wireless technologies tomorrow. They also receive access to the world’s leading wireless charging standards and development tools, and connect to a global community of companies working together to realize a vision of a world without wires.
Become a member of AirFuel Alliance to work with the world’s most innovative companies and build a global interoperable wireless power ecosystem.
